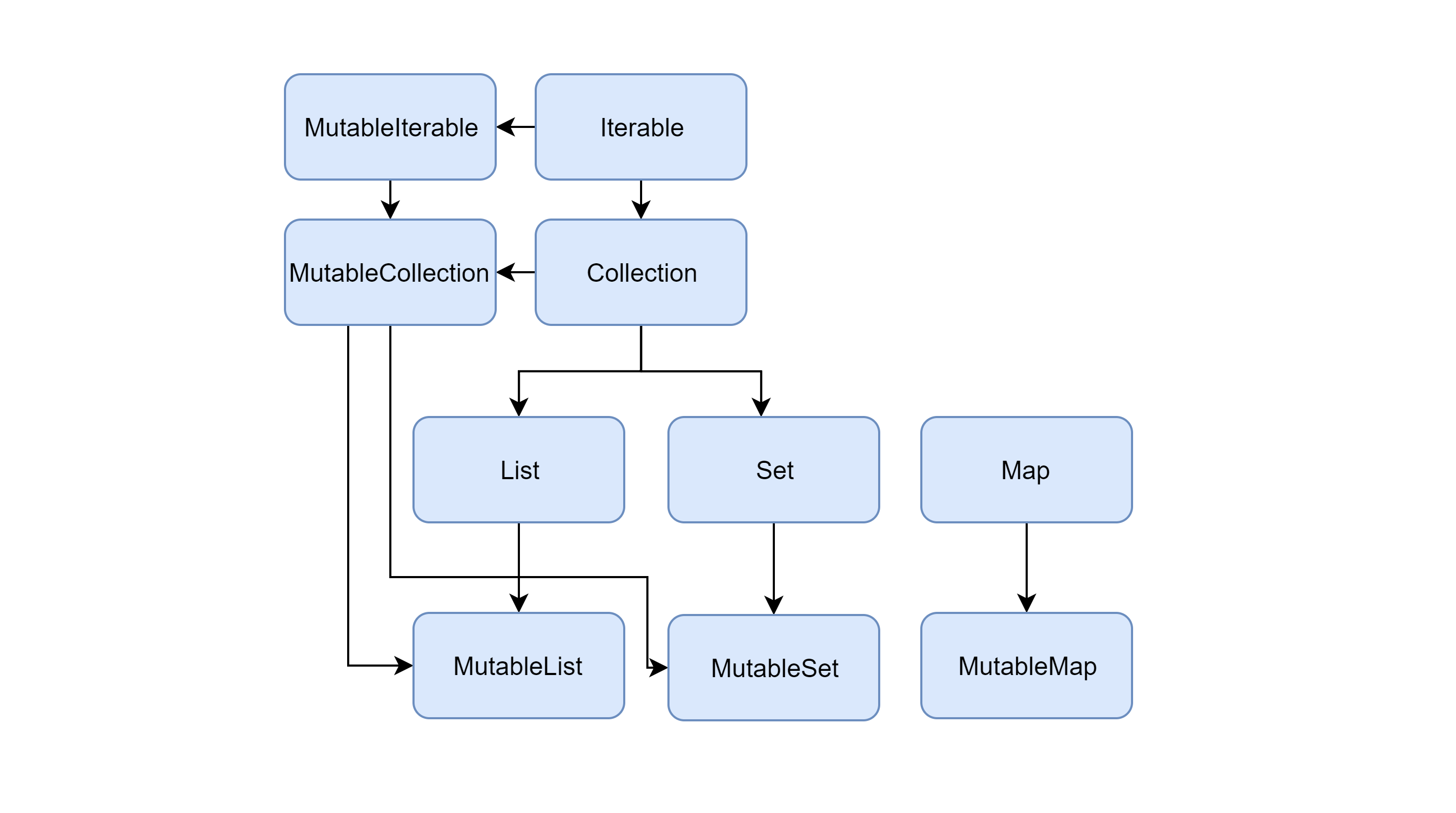
Data Structures in Kotlin
Kotlin provides a wide range of data structures to suit different needs. As Kotlin is interoperable with Java, you can also use Java’s collections in Kotlin code.
Array
An array is a fixed-size container for elements of the same type. Kotlin supports both generic (Array<T>) and primitive-specific arrays (IntArray, DoubleArray, etc.) for better performance. Arrays are zero-indexed and offer built-in functions like forEach, map, and filter for easy manipulation. Initialization can be done using arrayOf() or constructor syntax.
1
2
val array = arrayOf(10, 20, 30, 40, 50)
println(array[0]) // output: 10
Maps
A map is a collection of key-value pairs where each key is unique and is associated with exactly one value. Kotlin offers two primary types of maps:
Map<K, V>: A read-only map.MutableMap<K, V>: A map that supports modification operations.
Immutable Map
Mutable Map
The mutableMapOf() function creates a mutable map, allowing you to add, remove, or update key-value pairs after its creation.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
var map = mutableMapOf<String, Int>()
map["X"] = 10 // Adding / Updating a new key-value pair
map["Y"] = 20
println(map) // Output: {X=10, Y=20}
println(map.containsKey("Z")) // false
println(map.containsValue(10)) // true
map.remove("X") // Removing a key-value pair
mutableMap.clear() // Removes all entries