Machine Learning
Machine learning is a branch of Artificial Intelligence that focuses on developing models and algorithms that let computers learn from data without being explicitly programmed for every task.
Introduction
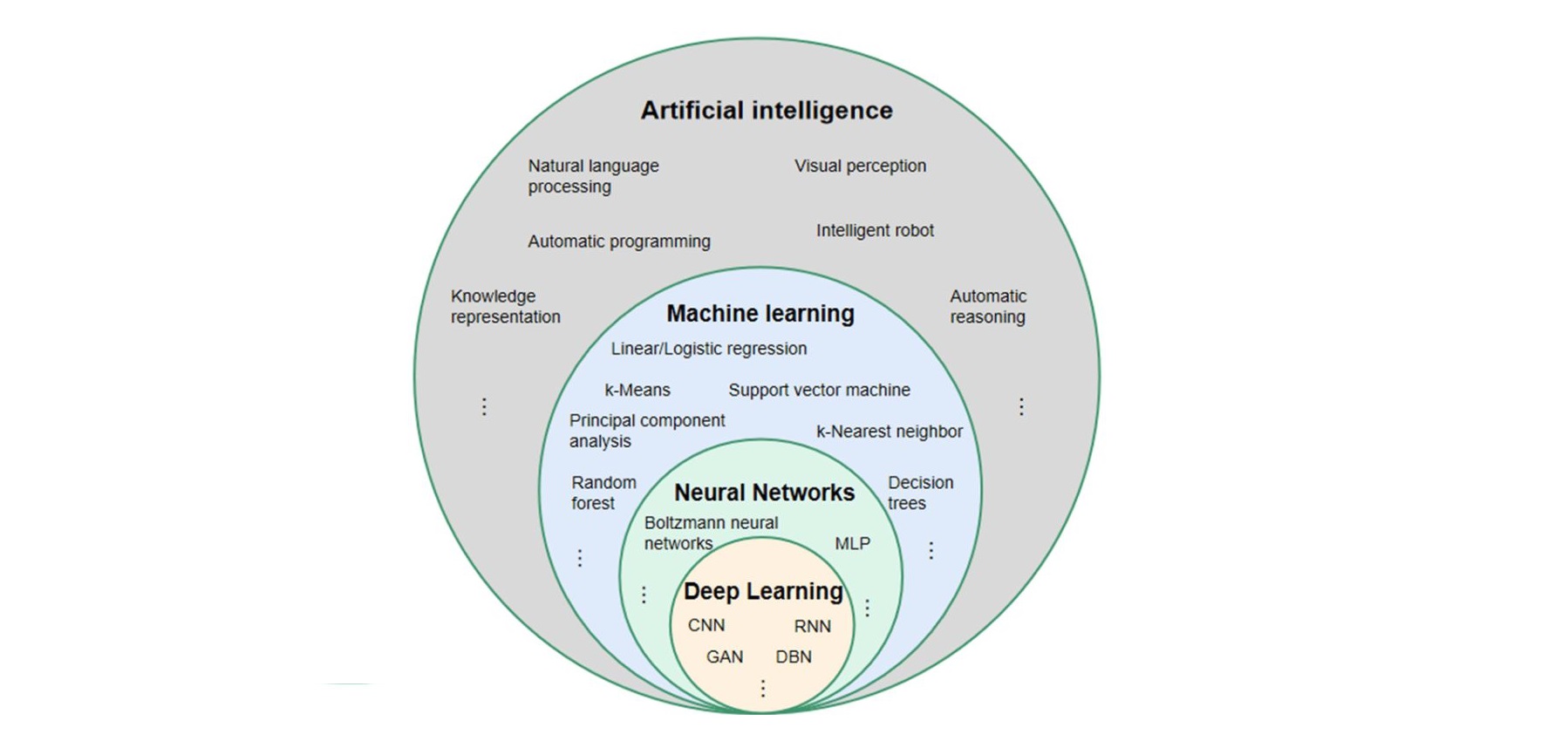
Artificial Intelligence (AI):
AI is the science of making machines think and act like humans. This includes problem-solving, decision-making, understanding natural language, and even recognizing patterns. AI can be rule-based (following pre-set logic) or learning-based, and it’s used in everything from chatbots to recommendation systems.
Machine Learning (ML):
ML is a part of AI where machines learn from data and get better over time without being directly programmed. It focuses on building algorithms that can find patterns in data and make predictions or decisions. For example, an ML model can learn to predict house prices based on past sales data.
Deep Learning (DL):
DL is a type of ML that uses neural networks to handle complex tasks like image recognition, speech, and language translation. It excels at handling large amounts of unstructured data like images, audio, or text. Deep learning powers advanced technologies like facial recognition, self-driving cars, and voice assistants like Alexa or Siri.
Computer Vision (CV):
Computer Vision is a field of AI that enables machines to see, understand, and interpret images or videos like humans. It’s used in things like facial recognition, object detection, and medical image analysis.
Natural Language Processing (NLP):
NLP is a branch of AI that helps machines understand, interpret, and generate human language. It’s used in chatbots, translation apps, speech recognition, and sentiment analysis.
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR):
ASR is a technology that converts spoken language into written text. It’s used in voice assistants, transcription services, and voice commands in apps and devices.
Supervised Learning
Supervised Learning is a type of machine learning where the model is trained on labeled data, meaning the input comes with the correct output. It learns to make predictions or classifications based on that. It’s used in tasks like spam detection, image classification, and loan approval.
Regression:
Regression is a type of supervised learning used to predict continuous values, like prices, temperatures, or sales. It finds the relationship between input features and a numerical output. For example, predicting house prices based on size and location.
Classification:
Classification is a type of supervised learning that assigns input data into categories or classes. For example, sorting emails into “spam” or “not spam,” or recognizing handwritten digits as numbers from 0 to 9.
Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised Learning is a type of machine learning where the model learns patterns from unlabeled data without specific answers. It’s used for grouping similar data (clustering) or reducing data dimensions, like customer segmentation or topic discovery.
Clustering:
Clustering is an unsupervised learning technique that groups similar data points together based on their features. It’s used to find patterns or segments in data, like grouping customers by buying behavior or organizing photos by similarity.
Reinforcement Learning (RL)
Reinforcement Learning is a type of machine learning where an agent learns by interacting with an environment and receiving rewards or penalties. It’s used in game-playing AIs, robotics, and self-driving cars to make decisions and improve performance over time.
Linear Regression
Linear Regression is a fundamental statistical method used to model the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables. It works by fitting a straight line through the data points that best represents this relationship. The goal is to minimize the error between the predicted and actual values using a technique called least squares. This method is commonly used in areas like finance, economics, and health science for predicting outcomes and identifying trends.